- August 18, 2023
- allix
- Research
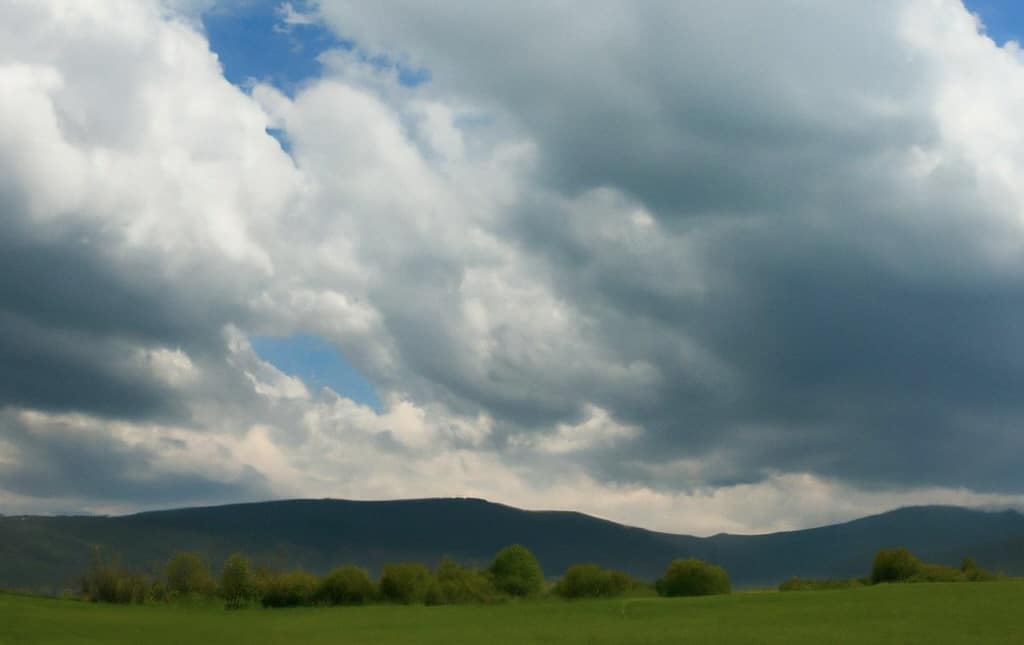
The existential threat posed by climate change has propelled it to the forefront of global concerns. As temperatures rise, ice caps melt, and extreme weather events become more frequent, humanity faces an urgent need to understand, mitigate, and adapt to these profound changes. Amid this critical juncture, the synergy between artificial intelligence (AI) and climate research has emerged as a beacon of hope. With its ability to process vast datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and optimize decision-making, AI is proving to be an invaluable asset in the fight against climate change.
Unraveling Complex Climate Patterns with AI
The climate is an intricate system governed by an array of interconnected variables. Deciphering the complexity of these patterns demands a level of computational power and analytical precision that AI can provide. By employing machine learning algorithms, researchers can sift through colossal datasets containing historical climate data, satellite imagery, and atmospheric measurements. This analytical prowess allows AI to identify subtle relationships, correlations, and trends that might escape human observation.
Consider the phenomenon of Arctic sea ice melt. AI algorithms can analyze decades of satellite images and temperature data to discern patterns of ice loss and predict future rates. Such insights are invaluable for understanding the impact of global warming on polar ecosystems, sea levels, and ocean currents.
AI’s computational capabilities enable it to simulate complex climate systems. By modeling the interactions between ocean currents, atmospheric circulation, and greenhouse gas emissions, researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of potential climate scenarios. These models are pivotal for predicting future changes, informing policy decisions, and designing adaptation strategies.
Climate modeling and prediction are pivotal for assessing the impact of climate change and devising strategies to mitigate its consequences. AI-driven models excel in their adaptability, learning from new data and refining their predictions over time. This adaptability enhances the accuracy of projections and equips scientists with the tools to address climate change’s multifaceted challenges.
Weather forecasting is a prime example of AI’s prowess in prediction. Modern meteorology heavily relies on AI algorithms that process real-time data from satellites, weather stations, and sensors around the world. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of information to generate accurate forecasts, thereby enhancing our ability to prepare for extreme weather events and minimize their impact.
Optimizing Energy Efficiency and Resource Management
One of the cornerstones of combatting climate change is the transition to cleaner energy sources and more efficient resource management practices. AI is at the forefront of driving this transition by optimizing energy consumption and utilization.
The energy sector, a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, benefits immensely from AI. Smart grids, powered by AI algorithms, enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution. These grids adjust energy flow based on demand patterns, optimizing energy distribution and minimizing wastage. AI aids in integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid, ensuring their efficient utilization.
Agriculture, too, is undergoing a transformation through AI. By analyzing data such as soil quality, weather patterns, and crop growth cycles, AI assists farmers in making data-driven decisions. These decisions range from optimizing irrigation schedules to predicting disease outbreaks and enhancing crop yield. Such precision agriculture practices contribute to increased efficiency, reduced resource consumption, and a more sustainable food supply.
Climate-Resilient Cities
As the global population gravitates toward urban centers, cities are becoming both focal points for climate change impacts and hotbeds for innovation. AI is instrumental in transforming cities into resilient and sustainable hubs.
Urban planning, traditionally guided by static data, is evolving through AI’s dynamic analysis. AI algorithms process urban data, including traffic patterns, demographics, and infrastructure utilization. This enables cities to optimize layouts, manage traffic congestion, and enhance public transportation systems. As a result, cities can reduce emissions, improve transportation efficiency, and create more livable environments for their residents.
AI-powered sensors contribute to the development of smart cities by monitoring air quality, noise levels, and energy consumption. These sensors provide real-time data, enabling cities to respond swiftly to pollution events, mitigate environmental risks, and enhance quality of life.
Companies Harnessing AI for Climate Research
A multitude of forward-thinking companies are leading the charge in harnessing the power of artificial intelligence to propel climate research and catalyze impactful environmental action. Among these innovators, one standout example is ClimateAI, a dynamic startup that leverages cutting-edge machine-learning techniques to elevate the accuracy of climate modeling. Through sophisticated data analysis and predictive algorithms, ClimateAI empowers scientists and policymakers alike to gain deeper insights into the intricacies of climate patterns. This enhanced understanding equips decision-makers with the knowledge they need to formulate informed strategies that address the pressing challenges posed by climate change.
Descartes Labs emerges as a trailblazer by employing AI-driven analyses of satellite imagery. Their efforts transcend mere data interpretation, as they delve into the heart of critical environmental issues. By scrutinizing satellite-derived data, Descartes Labs unveils hidden trends in deforestation, shifts in land use, and the ebb and flow of carbon emissions. These insights serve as invaluable tools for tracking the ever-evolving state of our environment, thereby facilitating the development of proactive preservation strategies that can mitigate ecological harm and promote sustainability.
Another towering example of AI’s potential in the realm of climate research is IBM’s visionary Green Horizon project. This ambitious initiative showcases the fusion of AI and Internet of Things (IoT) technology to revolutionize air quality predictions. By seamlessly integrating AI algorithms with a network of IoT sensors, the project focuses its gaze on the sprawling metropolis of Beijing. Through real-time data analysis and intricate modeling, Green Horizon aims to unravel the complex dynamics of air quality, a multifaceted challenge exacerbated by rapid urbanization and industrialization. This endeavor underscores AI’s ability to grapple with intricate environmental issues and offers a tangible demonstration of its capacity to address and potentially alleviate the complexities posed by urban pollution and environmental health hazards.
Categories
- AI Education (39)
- AI in Business (65)
- AI Projects (87)
- Research (107)
- Uncategorized (5)
Other posts
- Medical Treatment in Brazil: Advanced Healthcare, Skilled Specialists, and Patient-Focused Care
- Dental Treatment in China: Modern Technology, Skilled Dentists, and Comprehensive Care for International Patients
- Plastic Surgery in China: Advanced Aesthetic Medicine Supported by Precision, Innovation, and Skilled Specialists
- Ophthalmology in China: Advanced Eye Care Guided by Innovation, Expertise, and Patient-Focused Treatment
- Finding Care, Calm, and Confidence: Why Patients Are Looking Toward Beroun in the Czech Republic
- Choosing Health, Energy, and a New Future: Exploring Gastric Bypass in Diyarbakır, Turkey
- When Facial Hair Tells Your Story: Considering a Beard Transplant in Phuket, Thailand
- When Prevention Becomes Power: Understanding Liver Cirrhosis Risk and Modern Screening Approaches in Spain
- When the Abdomen Signals Something Serious: Understanding Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Getting Expert Evaluation in Islamabad
- When Back Pain Becomes More Than “Just Pain”: Understanding the Need for Microdiscectomy
Newsletter
Get regular updates on data science, artificial intelligence, machine